We are surrounded by different mobile devices such as iPhones, Samsung mobiles and a wide variety of tablets which are used on a daily basis at home and by businesses. Therefore, extracted digital evidence from these devices can have a critical role in supporting or defending a civil or criminal case in the courts. Mobile Device Forensics, which deals with data extraction and examination, has to be done properly and accurately. More than 80 percent of digital evidence is at risk of being thrown out of court without proper legal and ethical steps taken first. Some people think complex tools and clever hacks are what matter most, but the real test is how rigorously you handle privacy rights and documentation in data extraction from mobile devices before you even touch it. Mobile Device Forensics requires attention to detail and adherence to protocols.
Table of Contents
- Step 1: Assess Legal And Ethical Considerations
- Step 2: Prepare Equipment And Software Tools
- Step 3: Execute Data Acquisition From Mobile Devices
- Step 4: Analyse Extracted Data For Relevant Information
- Step 5: Verify Data Integrity And Document Findings
Quick Summary
| Key Point | Explanation |
|---|---|
| 1. Obtain Legal Authorisation First | Secure explicit permissions to ensure evidence is admissible in court and to protect privacy rights. |
| 2. Prepare Forensic Equipment Thoroughly | Use dedicated hardware and software to establish a reliable technological foundation for investigations. |
| 3. Implement Rigor in Data Acquisition | Conduct systematic extraction methods to preserve integrity and protect against data loss during evidence collection. |
| 4. Employ Advanced Data Analysis Techniques | Use structured frameworks to derive meaningful insights from digital evidence and detect hidden connections and narratives. |
| 5. Verify and Document Findings Meticulously | Conduct integrity checks and prepare detailed reports to maintain evidence credibility for legal scrutiny. |
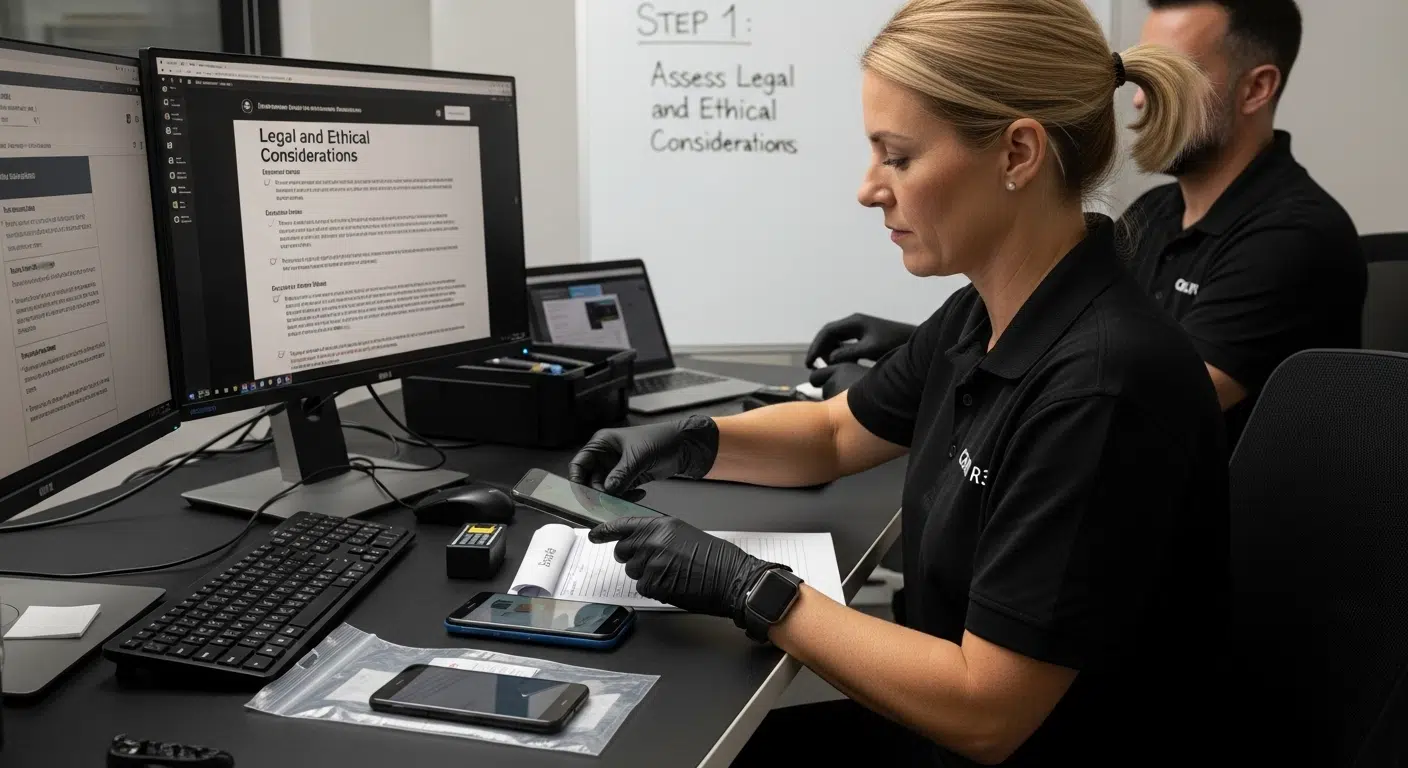
Step 1: Assess Legal and Ethical Considerations
Mobile device forensics demands rigorous legal and ethical preparation before any investigative procedure. Professionals must establish a comprehensive framework that protects individual privacy rights while ensuring the admissibility of digital evidence in legal proceedings.
The importance of Mobile Device Forensics cannot be overstated. As technology continues to evolve, so do the methods used in Mobile Device Forensics, making it imperative for professionals to stay updated with the latest trends and techniques.
Understanding Legal Parameters
Before commencing any mobile forensic investigation, practitioners must secure appropriate legal authorisation. This typically involves obtaining explicit warrants, court orders, or written consent from relevant stakeholders. The legal documentation must precisely define the scope of digital evidence collection, specifying which devices, data types, and timeframes are permitted for examination.
In the realm of Mobile Device Forensics, comprehending the nuances of different devices is crucial. Each mobile device may present unique challenges, hence a tailored approach is often necessary to effectively extract evidence.
According to National Institute of Justice research, forensic practitioners must meticulously document their investigative processes to maintain legal credibility. This documentation should comprehensively record:
- Chain of custody for digital evidence
- Forensic methodologies employed
- Tools and technologies used during investigation
- Specific data extraction and preservation techniques
Ethical Considerations in Digital Investigations
Ethical mobile device forensics transcends mere legal compliance. Professionals must actively protect individual privacy rights while pursuing legitimate investigative objectives. This requires implementing data minimisation principles, where only relevant and necessary information is collected and analysed.
Key ethical considerations include maintaining strict confidentiality, preventing unnecessary data exposure, and ensuring digital evidence is handled with utmost professional integrity. Investigators must continually balance the investigative requirements against potential privacy infringements, using surgical precision in their approach.
Successful completion of this step means having comprehensive legal authorisation, a clear investigative mandate, and a robust ethical framework that protects both the investigation’s objectives and individual privacy rights.
The ongoing advancements in technology have made Mobile Device Forensics an ever-evolving field, requiring continuous learning and adaptation from forensic professionals.
Step 2: Prepare Equipment and Software Tools
Mobile device forensics requires meticulous equipment preparation and strategic tool selection. This critical phase establishes the technological foundation for a successful digital investigation, ensuring investigators have reliable, forensically sound resources to extract and analyse digital evidence.
Essential Forensic Hardware Preparation
Begin by assembling a comprehensive forensic workstation with dedicated hardware designed for evidence preservation. Specialized forensic computers should feature write blockers, multiple evidence storage drives, and robust security configurations that prevent unintentional data modification. Select systems with substantial RAM, powerful processors, and extensive storage capabilities to manage complex digital forensic tasks.
According to National Institute of Standards and Technology guidelines, investigators must prioritize equipment that maintains forensic integrity. This involves using:
- Dedicated forensic laptops or workstations
- Hardware write blockers for physical device connections
- Multiple external storage drives with redundant backup capabilities
- Signal blocking containers to prevent remote device interference
Software Tools and Forensic Environments
Carefully curate a suite of forensically validated software tools capable of handling diverse mobile device ecosystems. Professional investigators require versatile solutions supporting multiple operating systems and device architectures. Preferred forensic software must offer comprehensive evidence collection, preservation, and analysis capabilities with robust chain of custody documentation.
Create a standardised forensic environment by installing reputable mobile forensic platforms that provide granular extraction methodologies. These tools should enable logical, physical, and advanced filesystem extractions while maintaining forensic image integrity. Critically, select software with regular update mechanisms to address emerging device security challenges and new extraction techniques.
Successful completion of this preparatory stage means establishing a forensically sound technological infrastructure. Investigators should verify their equipment’s operational status, confirm software licensing and compatibility, and perform preliminary system diagnostics. A well-prepared forensic workstation represents the foundational platform from which sophisticated digital investigations can be conducted with precision and reliability.
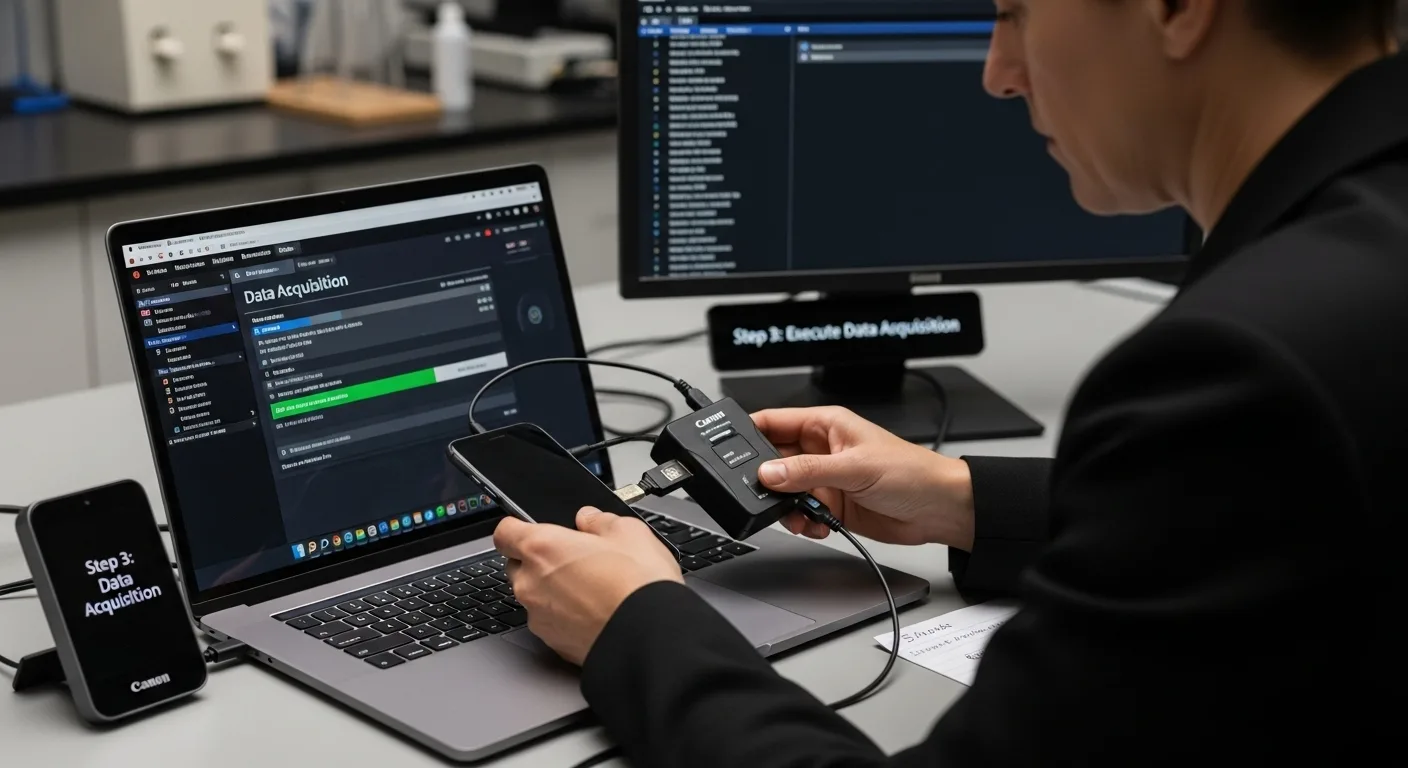
Step 3: Execute Data Acquisition from Mobile Devices
When conducting Mobile Device Forensics, it is essential to understand the specific tools and methodologies that cater to various operating systems and device types.
Data acquisition represents the critical moment where digital evidence is extracted with precision and forensic integrity. Investigators must approach this stage with methodical care, understanding that each device presents unique challenges and requires tailored extraction strategies.
Preliminary Device Examination
Mobile Device Forensics encompasses a variety of processes including data extraction, analysis, and documentation, all of which play a vital role in the investigation’s outcome.
Initiate the acquisition process by conducting a comprehensive initial assessment of the mobile device. Power state and connectivity are crucial considerations. If the device is powered on, carefully evaluate potential data volatility and determine whether a live or powered-down extraction method is most appropriate. Investigators must prevent unintentional data loss or modification during this critical phase.
According to NIST forensic guidelines, forensic practitioners should prioritise preservation techniques that maintain digital evidence integrity. This involves:
- Documenting device state and configuration
- Identifying device manufacturer and model specifics
- Assessing potential security mechanisms
- Selecting appropriate forensic extraction methodology
Extraction and Imaging Protocols
Choose extraction methods based on device characteristics, operating system, and available forensic technologies. Professional investigators typically employ multiple acquisition strategies to ensure comprehensive evidence collection. This might involve logical extractions for accessible data, physical imaging for complete device replication, or advanced filesystem parsing for complex mobile platforms.
Carefully connect the device to forensic workstations using write blockers and specialised forensic interfaces. Implement systematic imaging protocols that generate cryptographically verified forensic images, ensuring each extracted data set includes comprehensive metadata and hash validation. Systematically document every action, capturing precise timestamps, extraction methods, and tool configurations to maintain a defensible chain of custody.
Successful data acquisition requires meticulous attention to detail and adaptable technical expertise. Investigators should verify extraction completeness by comparing hash values, reviewing extracted data integrity, and confirming that all potential evidence sources have been comprehensively addressed. The goal is not merely collecting data, but ensuring that every digital artifact is captured with unimpeachable forensic standards.
Professionals in Mobile Device Forensics must be adept at employing different extraction techniques tailored to the device type, ensuring that evidence is gathered without compromising integrity.
The following table compares common mobile device data acquisition methods discussed in this guide, helping professionals determine the most appropriate approach based on device state and investigative requirements.
| Acquisition Method | Description | Suitable Scenarios | Key Considerations |
|---|---|---|---|
| Logical Extraction | Captures accessible files and data | Device powered on, no advanced encryption | May miss deleted or hidden data |
| Physical Imaging | Creates a complete replica of the device storage | Full evidence preservation needed | Requires specialist tools, longer process |
| Filesystem Parsing | Extracts file system structure and metadata | Advanced device configurations | Helps reconstruct deleted or fragmented data |
| Live Acquisition | Extracts data from a running device | Volatile data at risk during power down | Risk of data modification, must be careful |
| Advanced Parsing | Accesses complex app data and hidden artefacts | Encrypted or compartmentalised data | Requires expert-level forensic skills |
Step 4: Analyse Extracted Data for Relevant Information
Data analysis transforms raw digital artifacts into meaningful forensic intelligence. This intricate phase demands systematic investigation, employing sophisticated techniques to uncover critical evidence hidden within complex mobile device datasets.
The analysis stage in Mobile Device Forensics requires a keen understanding of data structures and the ability to interpret complex datasets accurately.
Structured Data Exploration
Begin the analysis process by establishing a methodical examination framework that systematically deconstructs extracted data. Investigators must approach digital evidence with a strategic mindset, understanding that seemingly insignificant fragments can reveal profound investigative insights. Leverage forensic software capabilities to parse through communication records, application metadata, geolocation information, and deleted content repositories.
Researchers recommend implementing a comprehensive analysis strategy that encompasses:
- Chronological data reconstruction
- Communication pattern identification
- Metadata cross-referencing
- Contextual evidence correlation
Advanced Forensic Interpretation Techniques
Professional forensic practitioners must go beyond superficial data examination, employing advanced analytical methodologies that uncover nuanced digital narratives. This involves utilising sophisticated forensic tools capable of reconstructing deleted messages, recovering fragmented files, and mapping complex digital interactions across multiple platforms and applications.
According to Digital Forensics Research Workshop guidelines, investigators should prioritise intelligent data correlation techniques. This means connecting seemingly disparate digital artifacts to construct comprehensive investigative timelines. Sophisticated analysis involves examining not just the content of digital communications, but also understanding the broader contextual relationships between different data points.
Through Mobile Device Forensics, practitioners can uncover vital information that may have a significant impact on legal proceedings.
Successful data analysis requires exceptional attention to detail, technical proficiency, and an investigative mindset that transforms raw digital information into actionable forensic intelligence. Verification of analysis completeness involves ensuring comprehensive coverage of available data sources, maintaining meticulous documentation of analysis processes, and preparing detailed forensic reports that can withstand rigorous legal scrutiny. The ultimate goal is to extract meaningful insights that support the investigation’s objectives while maintaining the highest standards of forensic integrity.
Step 5: Verify Data Integrity and Document Findings
Data integrity verification represents the cornerstone of forensically sound digital investigations. This critical phase transforms raw evidence analysis into a legally defensible documentation process, ensuring that every digital artifact can withstand rigorous legal scrutiny.
Comprehensive Evidence Validation
The process of validation in Mobile Device Forensics is crucial to ensure that all collected evidence maintains its forensic integrity throughout the investigation.
Initiate the verification process by conducting systematic integrity checks across all extracted digital evidence. Forensic practitioners must generate cryptographic hash values for each evidence file, comparing original and extracted data to confirm absolute consistency. These hash computations serve as digital fingerprints, providing irrefutable proof that no unintentional modifications occurred during the forensic investigation.
Professional investigators should document and validate:
- Cryptographic hash values for each evidence file
- Extraction timestamps and methodologies
- Device and data source specifications
- Potential chain of custody information
Forensic Reporting and Documentation
Craft a comprehensive forensic report that meticulously details the entire investigative process. The documentation must be transparent, objective, and structured to communicate findings clearly to legal professionals, investigators, and potential court audiences. Professional reports should provide a narrative that explains technical processes in accessible language while maintaining scientific precision.
According to NIST forensic guidelines, forensic documentation must include detailed provenance information demonstrating the reliability and authenticity of digital evidence. This involves creating a chronological account of every forensic action, including tool utilisation, extraction methodologies, and analytical processes.
Successful verification and documentation require an unwavering commitment to forensic best practices. Investigators should perform multiple integrity checks, cross-reference findings, and ensure that every digital artifact can be traced back to its original source. The final report must serve not just as a record of investigation, but as a robust, legally admissible document that can withstand intense professional and legal examination.
In conclusion, Mobile Device Forensics is a complex field requiring thorough understanding and application of various techniques to yield reliable and admissible evidence.
This table summarises key verification and documentation requirements outlined in Step 5, acting as a quick checklist for forensic practitioners to ensure legal defensibility of findings.
| Verification Step | Description | Purpose |
|---|---|---|
| Hash Value Generation | Compute cryptographic hashes for each evidence file | Confirm data integrity and authenticity |
| Extraction Documentation | Record timestamps, methodologies, and tool usage | Maintain transparent chain of custody |
| Device and Data Source Validation | Note device specifications and evidence origins | Support provenance for legal scrutiny |
| Detailed Forensic Reporting | Provide clear, structured narrative on all actions taken | Facilitate expert review and legal processes |
| Cross-Referencing of Findings | Compare and confirm insights from multiple data sources | Strengthen credibility and completeness |
Ready to Solve Your Toughest Mobile Forensics Challenges?
If you are struggling to ensure evidence integrity or navigating the legal and ethical complexities outlined in our guide, you are not alone. In the world of mobile device forensics, simple mistakes in data acquisition or documentation can make the difference between a case won or lost. The pain of uncovering critical mobile data only to find it is not admissible in court can be overwhelming. Get direct support from real Mobile Forensic Experts who understand every stage of the process—from legal authorisation and secure evidence collection to advanced analysis and expert reporting.
Bring clarity and confidence to your investigation. Visit Computer Forensics Lab to discover how our accredited team can help you handle chain of custody, data validation, and expert testimony. Take the first step now and find out how our Mobile Phone Forensics services can support your next case or corporate investigation.
Frequently Asked Questions
What legal authorisation is required for mobile device forensics?
Professionals must secure appropriate legal authorisation, typically through warrants, court orders, or written consent, which should define the scope of digital evidence collection.
How can I ensure the ethical handling of data during mobile forensics?
Implementing data minimisation principles is crucial. Only collect and analyse relevant information, maintain confidentiality, and ensure that evidence is handled with professional integrity to protect individual privacy rights.
What equipment is necessary for a mobile forensic investigation?
Establish a forensic workstation with dedicated hardware, including write blockers, external storage drives, and forensic computers that maintain forensic integrity and are configured for security and performance.
What methods are used to acquire data from mobile devices?
Data acquisition methods depend on the device’s characteristics and operating system. Common techniques include logical extraction for accessible data, physical imaging for complete replication, and advanced filesystem parsing to access complex data structures.

