More than 90 percent of legal cases now involve some form of digital evidence, making computer forensics workflow a crucial skill for investigators and legal professionals. The rise in cybercrime and data breaches has transformed the way digital evidence is collected, analysed, and presented in court. Understanding these forensic processes helps ensure every piece of evidence stands up to legal scrutiny and supports strong, defensible outcomes in modern investigations.
Table of Contents
- Defining Computer Forensics Workflow
- Stages of Digital Evidence Collection
- Analysing and Interpreting Digital Data
- Legal Standards and Chain of Custody
- Expert Witness Reporting and Court Usage
- Common Mistakes in Forensics Workflow
Key Takeaways
| Point | Details |
|---|---|
| Workflow Stages | The computer forensics workflow consists of evidence identification, collection, examination, and reporting, ensuring legal integrity throughout the process. |
| Digital Evidence Collection | Rigorous adherence to structured collection methods is vital to maintain evidence integrity and legal admissibility during investigations. |
| Chain of Custody | Maintaining a meticulous chain of custody is crucial for preserving the integrity and authenticity of digital evidence throughout the legal process. |
| Expert Reporting | Expert witness reporting must convey complex findings clearly and objectively, aligning with legal standards to support judicial proceedings. |
Defining Computer Forensics Workflow
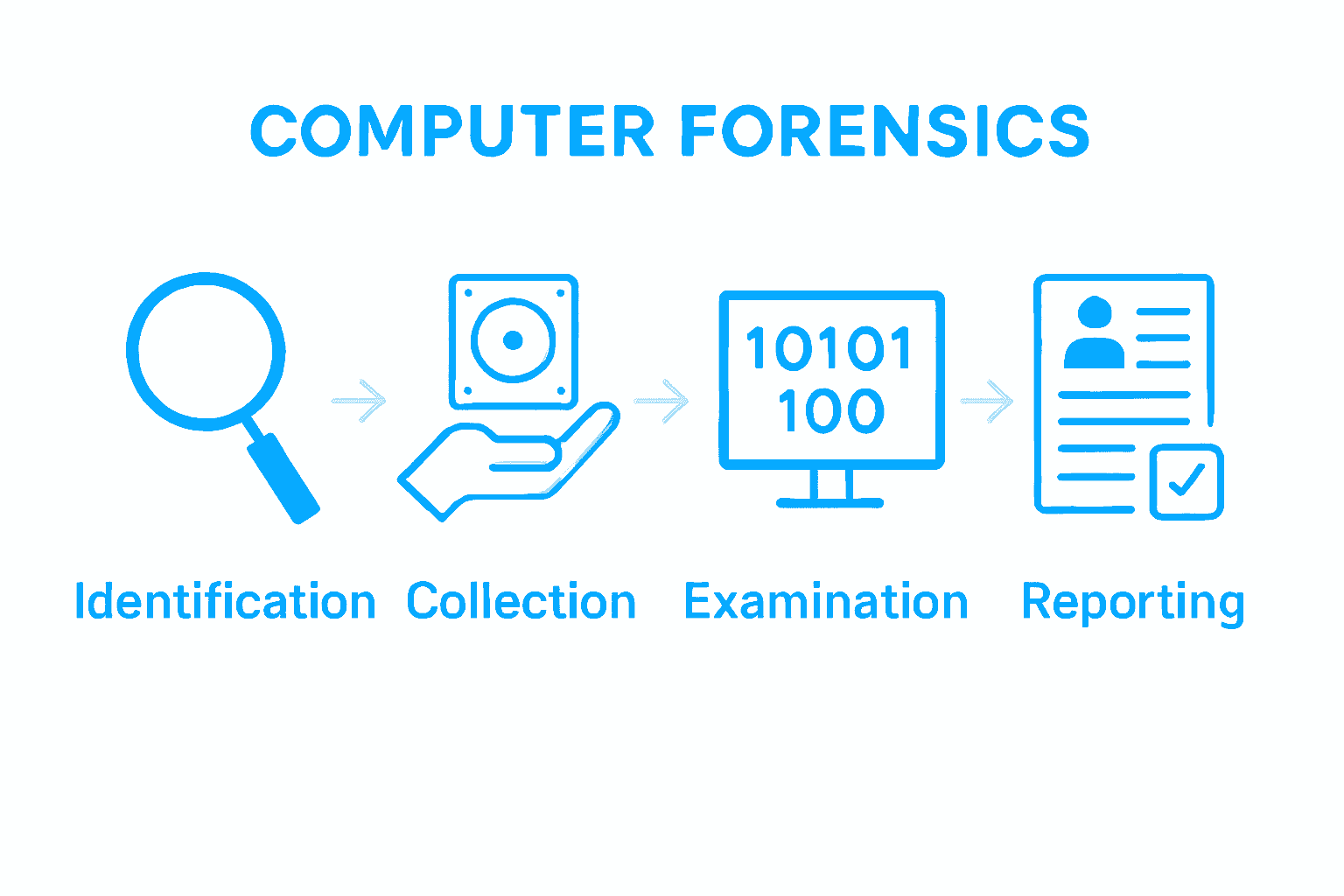
Computer forensics workflow represents a systematic process of collecting, preserving, analysing, and presenting digital evidence in a manner that maintains legal integrity and supports investigative objectives. According to research from arxiv, digital forensic process models provide comprehensive frameworks for conducting thorough and legally defensible investigations.
The workflow typically encompasses several critical stages that ensure meticulous handling of digital evidence. unafei outlines these key stages as:
- Evidence Identification: Locating potential digital sources of evidence
- Evidence Collection: Carefully extracting digital artifacts while maintaining forensic integrity
- Evidence Examination: Conducting detailed technical analysis of collected data
- Evidence Reporting: Documenting findings in a clear, professional manner suitable for legal proceedings
Successful computer forensics workflow demands rigorous attention to detail and adherence to standardised investigative protocols. Each stage requires specialised skills, advanced technological tools, and a methodical approach to ensure that digital evidence remains admissible and reliable in legal contexts. Forensic specialists must navigate complex technical challenges while simultaneously maintaining strict chain of custody procedures that preserve the evidential value of digital information.
Stages of Digital Evidence Collection
Digital evidence collection represents a critical phase in forensic investigations, requiring precision, methodical approach, and strict adherence to legal standards. ijcaonline emphasises the paramount importance of maintaining data integrity throughout the evidence gathering process.
The digital evidence collection process typically follows a structured sequence of stages, as outlined by dergipark:
- Initial Assessment: Determining the scope and nature of digital evidence required
- Preservation: Securing the original digital environment without modification
- Identification: Locating and documenting potential sources of electronic evidence
- Collection: Carefully extracting digital artifacts using forensically sound methodologies
- Transportation: Securely transferring collected evidence to forensic laboratory
- Storage: Maintaining evidence in controlled, protected environments
Successful digital evidence collection demands sophisticated technical skills and meticulous documentation. Forensic specialists must employ advanced techniques such as write blockers, create forensic disk images, and maintain comprehensive chain of custody logs to ensure the legal admissibility of digital evidence. These rigorous protocols protect against potential challenges to evidence authenticity and support comprehensive legal investigations.
To ensure thorough digital evidence collection, forensic professionals must develop step by step digital evidence collection guide skills that encompass both technological expertise and procedural knowledge. This approach guarantees that digital evidence remains intact, traceable, and legally defensible throughout the investigative process.
Analysing and Interpreting Digital Data
Digital data analysis is a sophisticated process that demands precision, advanced technological tools, and expert forensic knowledge. arxiv highlights the critical importance of developing robust methodologies for preserving and interpreting digital evidence across complex technological environments.
Forensic specialists employ multiple sophisticated techniques to extract and interpret digital data:
- File System Analysis: Examining directory structures and metadata
- Metadata Extraction: Recovering hidden information about digital artifacts
- Timeline Reconstruction: Mapping chronological sequences of digital events
- Pattern Recognition: Identifying anomalies and suspicious digital activities
- Cryptographic Analysis: Decoding encrypted communication and files
Tools play a pivotal role in digital forensics. en demonstrates how specialised software libraries enable forensic experts to extract and parse complex data from various digital storage systems. These utilities allow investigators to recover deleted files, analyse disk images, and reconstruct digital timelines with remarkable accuracy.
To enhance investigative capabilities, forensic professionals can explore what is forensic data analysis techniques that provide deeper insights into digital evidence interpretation. Understanding these advanced methodologies ensures comprehensive and legally admissible digital forensic investigations.
Legal Standards and Chain of Custody
Chain of custody represents the fundamental legal mechanism ensuring the integrity and admissibility of digital evidence in judicial proceedings. arxiv highlights emerging technological approaches, such as blockchain-based systems, that are revolutionising how forensic professionals document and track digital evidence throughout investigations.
The chain of custody process involves several critical documentation requirements:
- Evidence Identification: Precise initial documentation of digital artifacts
- Preservation: Maintaining original evidence in unaltered condition
- Tracking: Recording every interaction and transfer of evidence
- Authentication: Verifying the integrity of digital materials
- Reporting: Creating comprehensive logs of evidence handling
arxiv emphasises that modern digital forensics must navigate increasingly complex technological landscapes, requiring sophisticated approaches to maintaining legal standards. Forensic specialists must meticulously document each stage of evidence handling, ensuring that digital artifacts remain legally defensible and scientifically verifiable.
To navigate these intricate legal requirements, forensic professionals can gain deeper insights through our complete guide to digital forensics chain of custody, which provides comprehensive strategies for maintaining impeccable evidence management protocols that withstand rigorous legal scrutiny.
Expert Witness Reporting and Court Usage
Expert witness reporting represents a critical intersection between technical forensic analysis and legal proceedings, requiring precision, clarity, and comprehensive documentation. journals highlights the pivotal role forensic experts play in translating complex digital evidence into understandable courtroom testimony.
The expert witness reporting process typically involves several crucial components:
- Technical Analysis: Detailed examination of digital evidence
- Methodology Documentation: Explaining investigative techniques
- Objective Interpretation: Presenting unbiased scientific findings
- Visual Representation: Creating clear graphical evidence summaries
- Legal Compliance: Ensuring forensic reports meet judicial standards
en introduces advanced forensic techniques like stochastic forensics, which enable experts to reconstruct digital activities even when traditional artifact evidence is limited. This approach allows forensic specialists to provide comprehensive insights that bridge technological complexity and legal requirements.
Legal professionals seeking deeper understanding can explore our computer forensics expert witness guide, which provides comprehensive strategies for preparing and presenting digital forensic evidence in criminal and civil proceedings.
Common Mistakes in Forensics Workflow
Digital forensic investigations demand absolute precision, with even minor errors potentially compromising entire legal proceedings. arxiv critically evaluates digital forensic process models, highlighting the significant risks associated with workflow mistakes that can undermine evidence reliability.
Common critical mistakes in forensic workflows include:
- Improper Evidence Handling: Compromising digital evidence integrity
- Inadequate Documentation: Failing to record comprehensive investigation steps
- Insufficient Technical Validation: Neglecting rigorous evidence verification
- Poor Preservation Techniques: Risking data contamination or loss
- Inconsistent Methodology: Deviating from established forensic protocols
unafei emphasises that contemporary digital forensic investigations require meticulous attention to procedural standards. Forensic specialists must develop robust mechanisms to prevent workflow errors that could potentially render critical evidence inadmissible in legal proceedings.
To mitigate these risks, forensic professionals can explore top digital forensics techniques that provide comprehensive strategies for maintaining investigative integrity and avoiding common procedural pitfalls in digital evidence collection and analysis.
Master the Computer Forensics Workflow with Expert Support
Navigating the complete computer forensics workflow can be complex and demanding. From meticulous evidence collection to maintaining a strict chain of custody and delivering expert witness reports, every step must be precise to ensure digital evidence remains legally admissible. If you face challenges such as improper evidence handling or need to strengthen your investigative process, understanding the detailed stages like preservation, identification, and digital data analysis is vital to your success.
Our Digital Forensics services at Computer Forensics Lab are designed to assist legal professionals, law enforcement, and businesses in overcoming these challenges. With advanced expertise in handling computing devices, cloud data, and mobile phones, we help you preserve data integrity and create comprehensive expert reports. Don’t let procedural risks impact your case results. Visit our website now and explore how our Chain of Custody Tracking solutions maintain the fullest legal compliance throughout your investigations.
Make sure your digital forensic efforts meet the highest professional standards and secure your vital evidence today.
Frequently Asked Questions
What is the computer forensics workflow?
The computer forensics workflow is a systematic process for collecting, preserving, analysing, and presenting digital evidence while maintaining legal integrity and supporting investigative objectives.
What are the key stages of digital evidence collection?
The key stages of digital evidence collection include initial assessment, preservation, identification, collection, transportation, and storage of electronic evidence to ensure data integrity and legal admissibility.
How is digital data analysed in forensics?
Digital data analysis involves techniques such as file system analysis, metadata extraction, timeline reconstruction, and pattern recognition to extract and interpret digital information effectively.
Why is chain of custody important in digital forensics?
Chain of custody is crucial as it ensures the integrity and admissibility of digital evidence in legal proceedings by meticulously documenting all evidence handling, tracking, and authentication processes.